A well-designed user interface increases the time your visitors spend on your website. How to design your UI correctly you can learn here! ... Continue reading


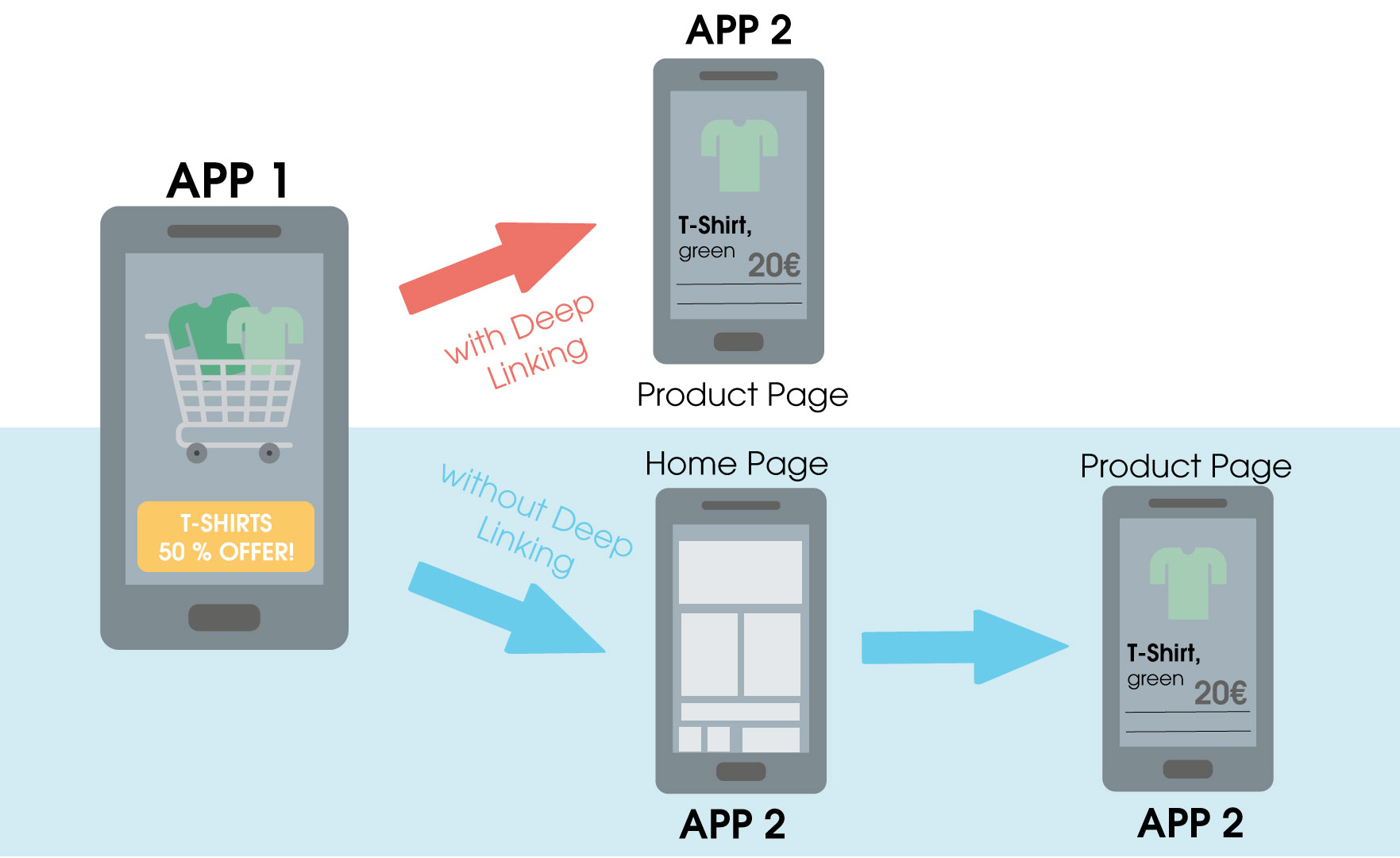
Deep links are hyperlinks that, unlike a homepage or surface link, take the user directly to a specific subpage of the visited website. They facilitate navigation and make content more accessible. In addition, deep links are valuable from an SEO point of view: with their help, traffic can be directed to specific subpages that are relevant to the user. As a result, linkjuice is passed on to them. In Google, deep links are mostly played out in the form of rich snippets.
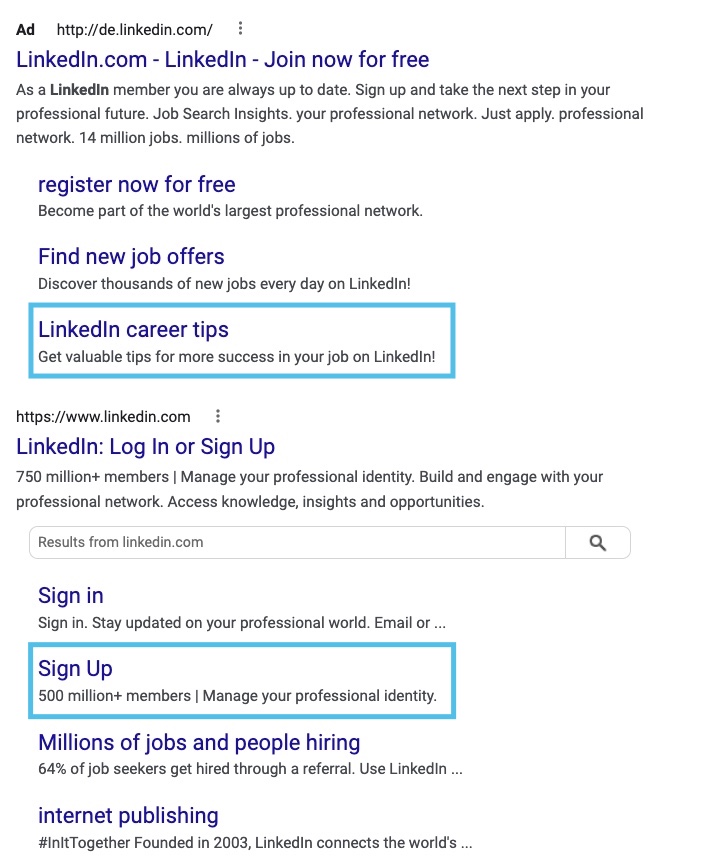
Deep links pass on the so-called linkjuice, a measure of the link strength of the links, to subpages. Therefore, they are used in Search Engine Optimization to strengthen targeted content on subpages, and thus the long tail.
However, it is important to ensure that a natural ratio between deep links and surface links is maintained. If the ratio is too unbalanced, for example, because almost only deep links and no start page links are used, this may be interpreted by Google as an attempt at manipulation and penalized. Accordingly, both the quality and quantity of the links, as well as the ratio between deep and surface links should be correct in order to achieve the best possible effect.
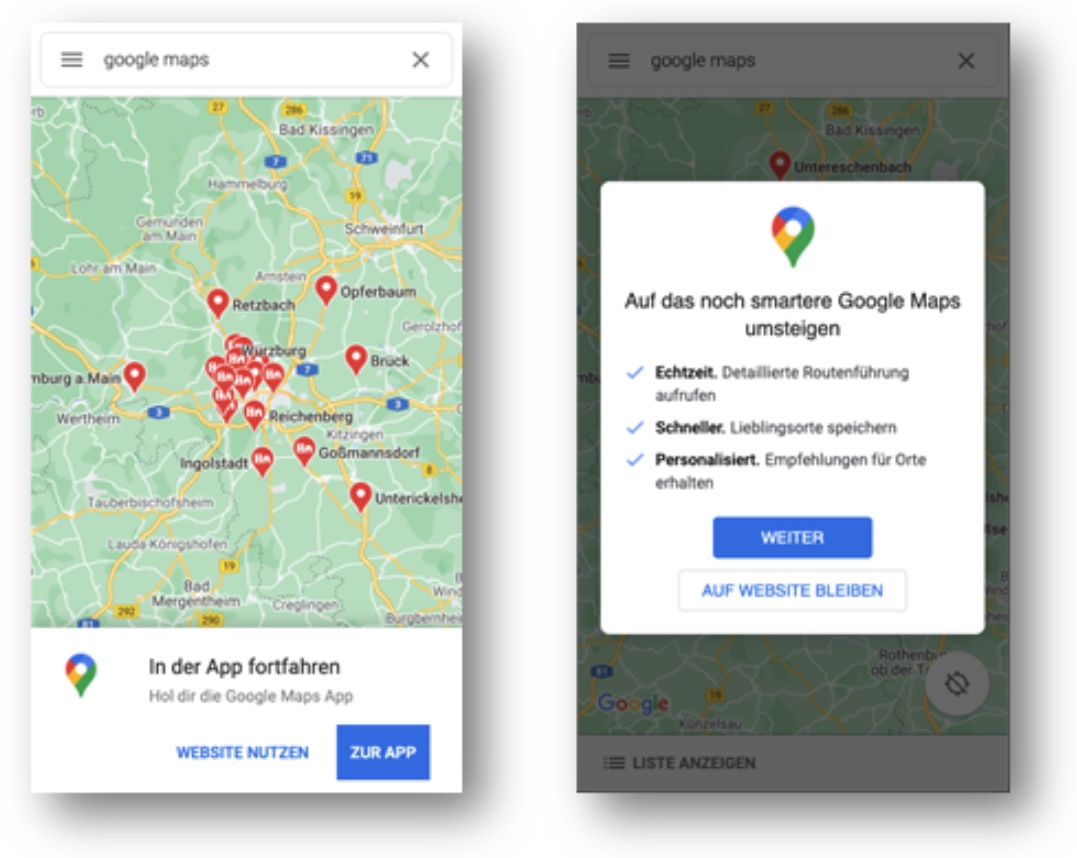
Deep linking on mobile devices benefits from enhanced functionality: Instead of URLs, mobile apps work with URIs, i.e. Uniform Resource Identifiers. This allows the user to use the deep link to open a preinstalled mobile app or to navigate directly to a specific screen in the mobile app.
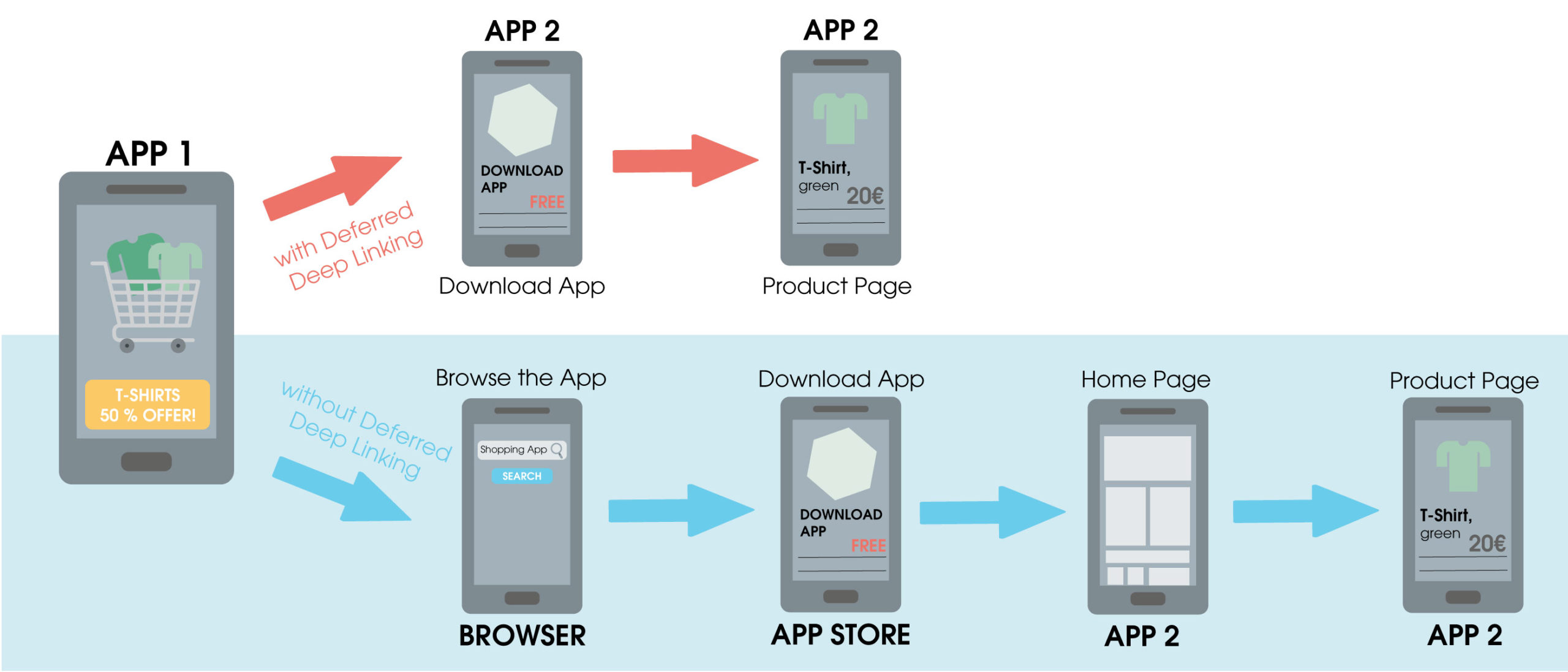
In addition, so-called delayed or deferred deep links can be used. These first check whether the desired mobile app is preinstalled on the end device and then redirect to the page within the app accordingly. If the app is not yet installed, the download page can be referred to directly.
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
|---|---|
| • Allow website users to find the content they want more easily | • Extreme deviation from the deep link ratio can lead to Google penalization |
| • Improve the relevance of a website for search engine results by optimizing the internal page structure and linking to relevant content | |
| • Help build authority for that page. If you have created an outstanding content like a blog post or article, the more links from high quality websites pointing to that particular page, the higher it can rank in a search engine. This can be used for lead generation. | |
| • Optimize the user experience. When a user is consuming content on another website and clicks on a link, they want to be directed to the most relevant information depending on their expectations. If they arrive at your homepage via a link and have to look around for what they expect, user frustration can increase and cause them to bounce. | |
| • Improve long tail phrase rankings. Long tail keywords are search queries with at least three to four words. These tend to be very specific. While they don’t get as much traffic as general keywords, they tend to have a higher conversion rate when the content matches the keyword search. |
You want to learn more about exciting topics?