The Robots.txt is used to control the crawling behavior of bots. What it has to do with it you will learn here with us! ... Continue reading


You probably know the hyperlink by the short term link. Both, however, refer to the same thing, namely a link or cross-reference within websites or (electronic) documents. The only requirement is that the link target has a unique address. Hyperlinks are typical for the internet and at the same time also its basis, since the World Wide Web lives from the structure and the linking of different pages.
You can recognize a link by the fact that it is usually highlighted (in color) and underlined.
It consists of the anchor text, that is, what you ultimately click on, and a stored, invisible URL. If you work in the HTML code of a website, you will find links as attributes that refer to the corresponding page or document.

Clicking on a link takes you to the link target, i.e. the linked page or the stored document. The link target can be a video, a website, media content or PDF documents.
There are different types of links. Especially with regard to search engine optimization, it is important to distinguish between internal and external linking.
Internal links are links from one of your own landing pages to another page on your website. The link target is therefore always within the same domain. For example, you can publish your homepage or relevant information about your company in the header. In the footer you can, for example, make the “imprint” or the contact directly accessible. This allows your website visitors to reach the most relevant pages from any point on the website. In addition, you can refer to further information on the relevant content in the body text. This ensures that your visitors receive added value. In addition, it ensures that they click through different pages, which increases the click-through rate and length of stay.
External links, also called outbound links, refer to all links that go from your website to another domain. These are therefore outbound external links. By linking to other domains, you can provide your users with further information on a topic and thus offer them added value. A distinction is made between surface and deep links. The former links to the start page or other landing pages. It therefore remains a rather superficial link. The latter links more deeply to a very specific subpage, media or to a download link of a PDF.
Another form of external links are backlinks. These are inbound external links. This means that an external domain refers to yours. Here, too, there are different forms that can be differentiated between:
Independent of internal or external links, there are links that have specific goals. For example, you can use a link to insert jump marks within your website. This takes users to a specific passage of text.
In addition, downloads or images/media can be opened via links. In addition, you can start writing an e-mail via a hyperlink. This opens the user’s e-mail program and your e-mail address is already stored as the recipient.
There are four different link structures in which an internal hyperlink can be constructed. This allows you to influence the behavior of the website visitors.
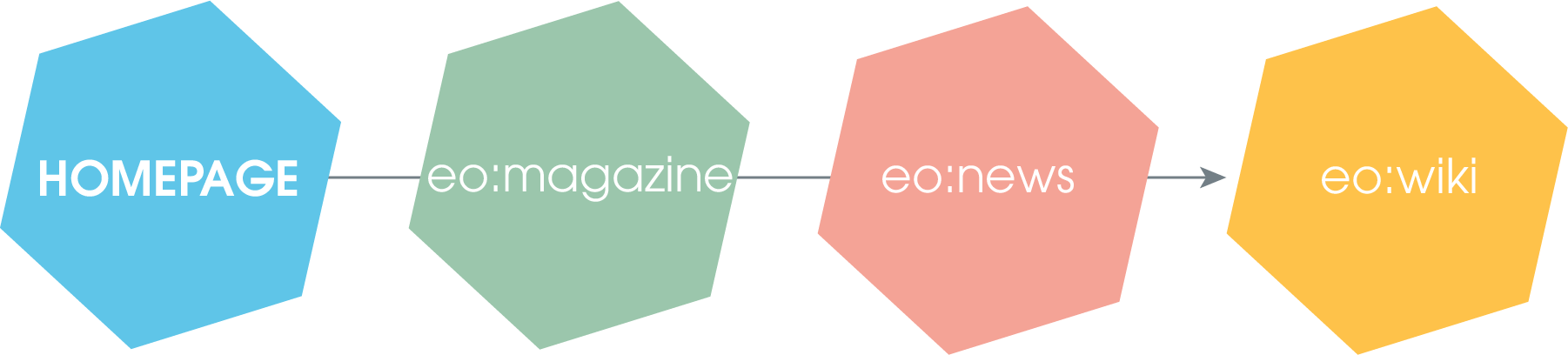
A linear link structure leads your website visitors from one page to the next in a “straight line”. They click through the link text to the next page. This is the case with normal links within body text in blogs, for example. With this structure, you have the most control over where your website visitors end up.
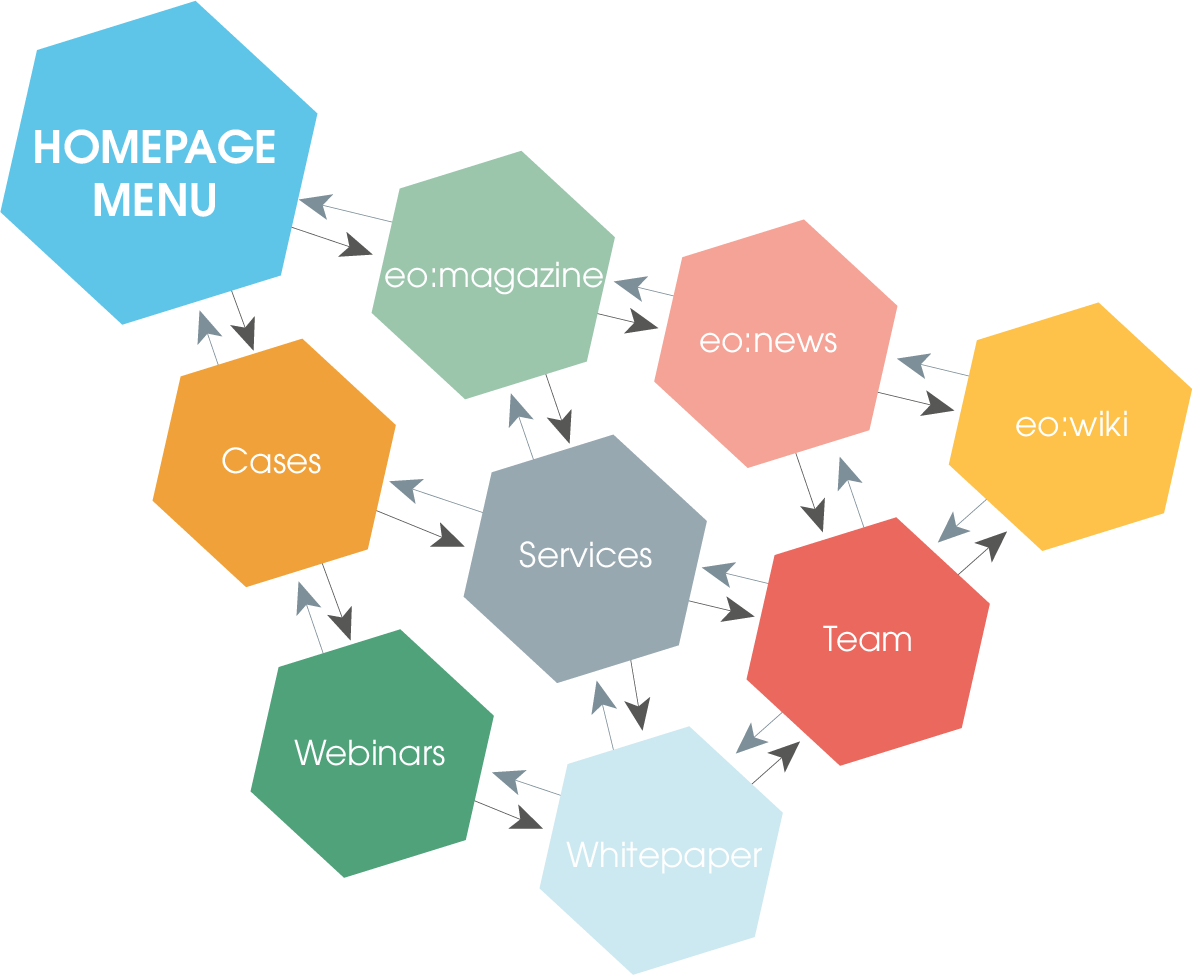
If a link is created in the network structure, you can reach any page from any starting point. However, you can also jump from another page (here, for example, from the webinar landing page) to another page on the website (e.g. eo:magazine) at any time. All pages of the website are thus linked to every other landing page. You have this case, for example, in website menus that a user can access from every landing page or from the menus of online shops.
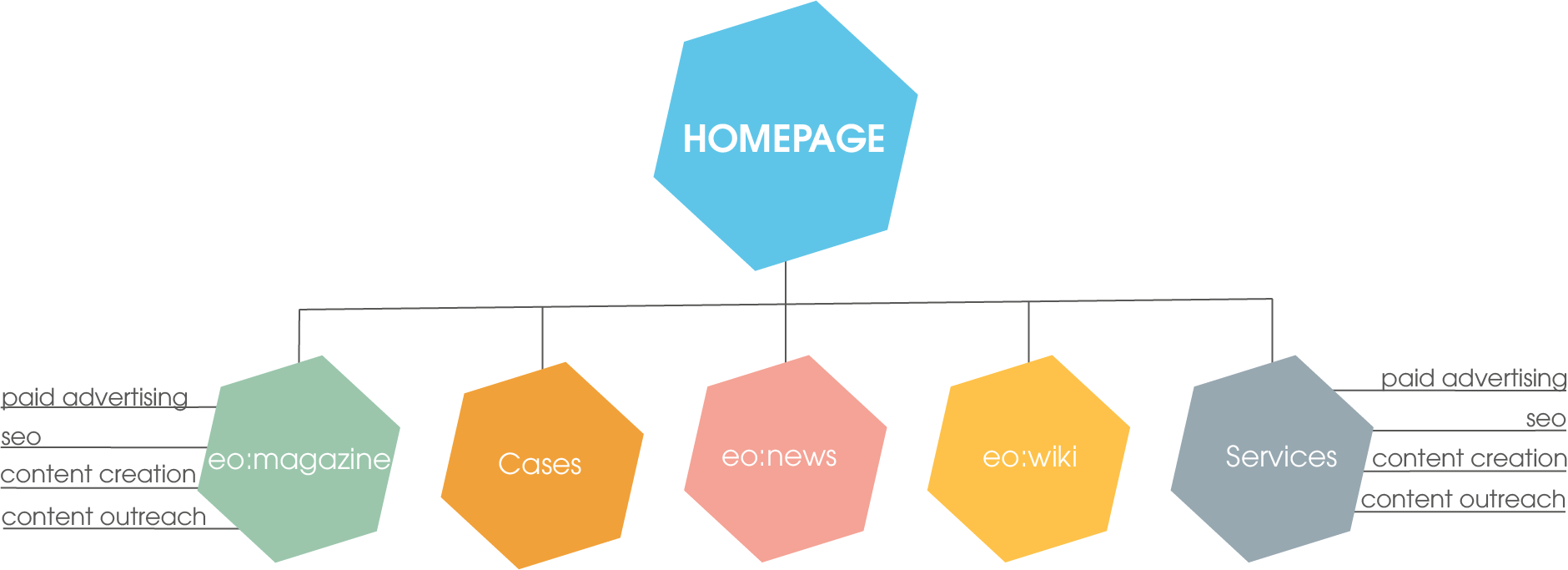
With the help of the tree structure, you can go from one top page to other sub-pages. A clear hierarchical structure is thus recognizable. The website is structured. This rather simple structure is often used in simple navigation bars or in web shops. The user always lands on the start page and then clicks via the category (e.g. “services”) to the individual product pages (e.g. SEO).
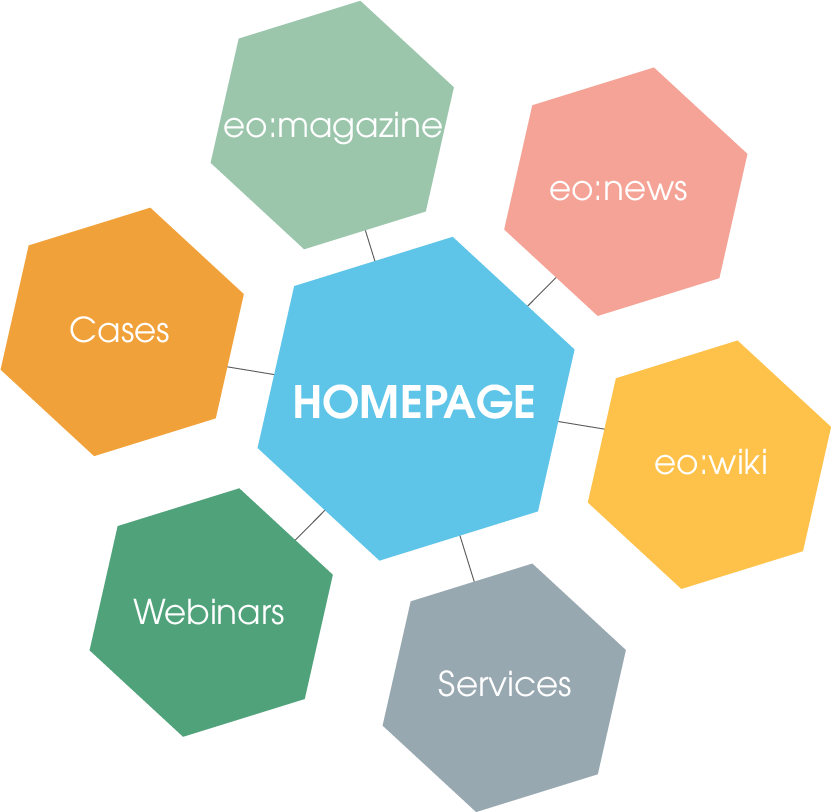
You use the star structure if you want to link many other contents from your content. This means that many different topic-relevant links start from one page, in which, for example, further terms are explained and thus give the user added value. You can find such structures in encyclopedias, for example.
In principle, you can link anything. You should just make sure that the linked content is relevant to your content. They should offer the user added value and provide them with high-quality information. When it comes to links, quality always comes before quantity. This will also help you improve your ranking.
You want to learn more about exciting topics?