Cloaking is a technique in which a website provides different content for search engines and human visitors. Learn more about it. ... Continue reading


Google PageRank is an algorithmic evaluation system for the linking structure of a website in order to draw conclusions about how important it is for users and the search engine. The method is based on a logarithmic function and the usage behavior of an average Internet surfer.
The two inventors of the Google algorithm, Larry Page and Sergei Brin, developed the PageRank algorithm in 1996 at Standford University and patented it one year later. Based on this method, the Google search engine as we know it today was created.
According to the two developers, Google PageRank is one of the 100 most important ranking factors in SEO. Therefore, you should see the Google PageRank algorithm as relevant and consider it in all your SEO measures.
The methodical procedure of the PageRank algorithm can be explained in such a way that a web user follows a link on the web page by chance and thus gets from there to another web page. Since the normal user does not follow all links up to the last link level, the PageRank algorithm also only follows a certain number of links until he finally stays on a web page. It is exactly this procedure that the “Random Surfer Models” is supposed to illustrate in more detail.
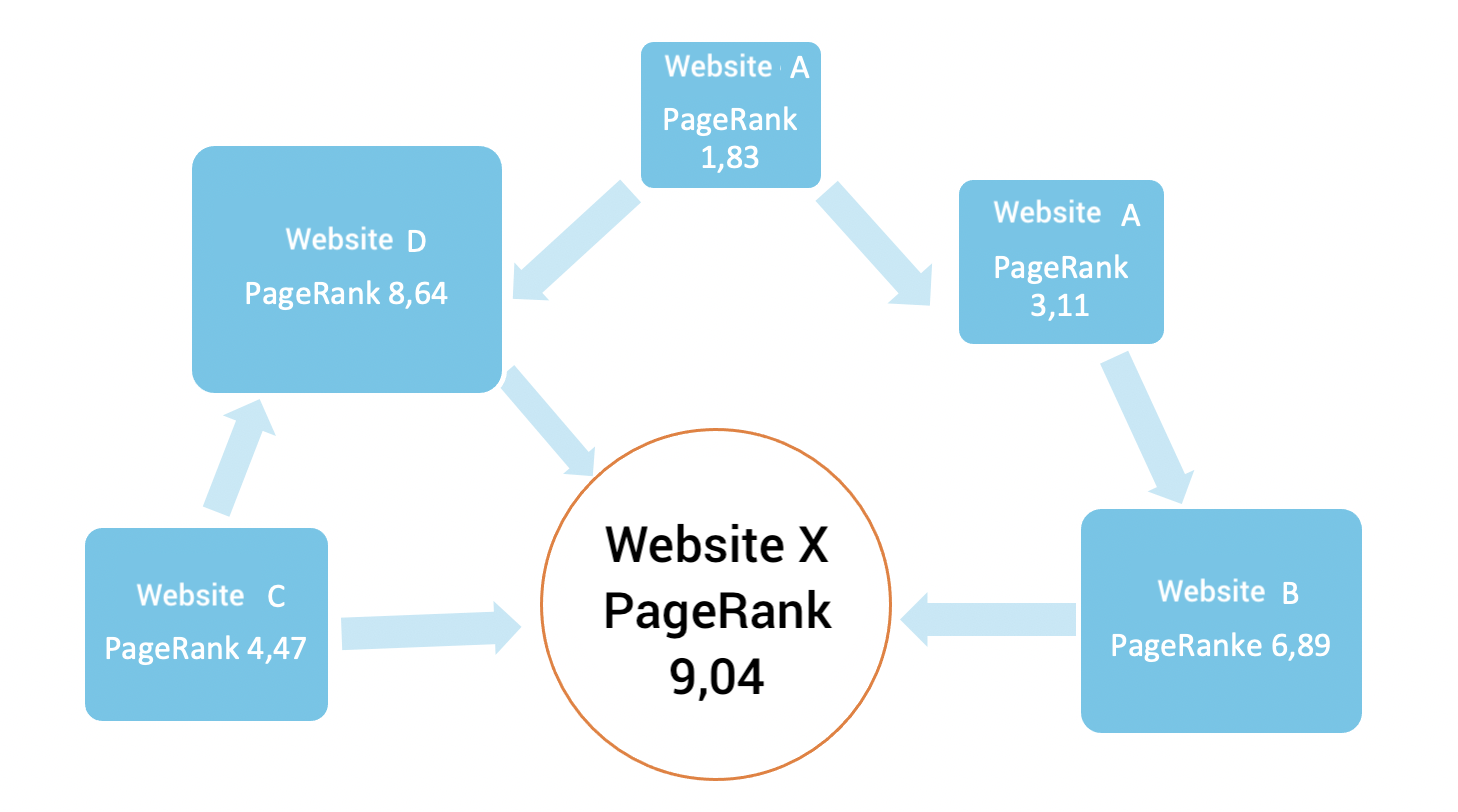
The more frequently a website is linked to from other domains, the more likely Google is to consider this website an important page. Both the content and the domain are relevant for Google. The procedure makes a basic distinction between quality and quantity. If your inbound links are from highly ranked websites, this will also have a positive effect on your Google PageRank. The “good” website thus bequeaths you some of its reputation. The result: Your rating increases.
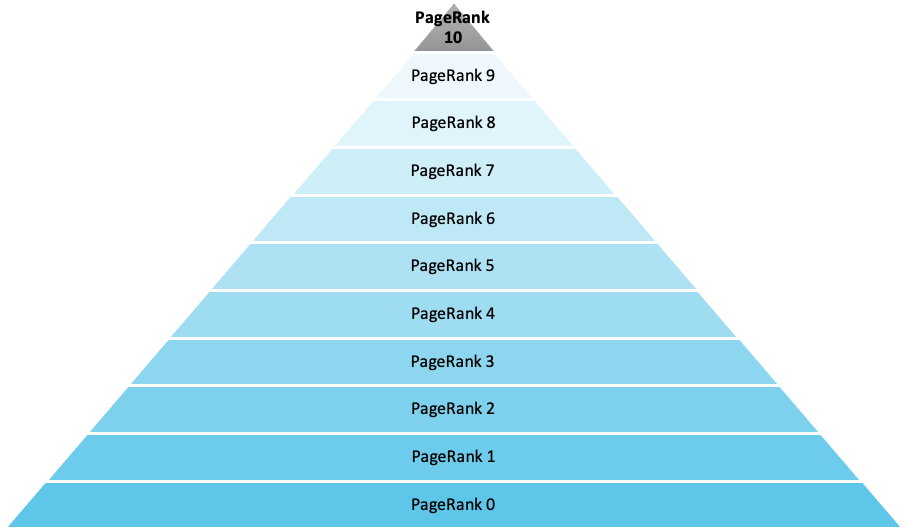
The rating of a website follows a scale from 0 to 10. The higher your PageRank is determined by your incoming links, the more important your domain seems to be for Google and the higher is your own PageRank value. The following applies:
PageRank 0 = lowest possible PageRank rating
PageRank 10 = highest possible PageRank rating
However, you should know that Google’s internal calculation is defined in decimal numbers and is therefore much more accurate than shown above.
The algorithm is an exponential function. This means that it is generally much more difficult to improve an already very good rating. Comparatively poor ratings, on the other hand, can be increased by just a few qualified links. Example: To go from an 8.34 rating to 9.52, you need many high-quality links that have at least a similarly good, if not even better PageRank than your page. On the other hand, it takes fewer high-quality or qualified links to go from PageRank 0.27 to PageRank 0.65.
It should be noted that the PageRank algorithm, like many algorithms, is constantly optimized. New updates can change the algorithm enormously and thus also influence your website negatively or positively. Therefore, you should constantly keep an eye on your website and especially your PageRank rating and intervene immediately if you see optimization potential.
In the past, this value was visible in the Google Toolbar PageRank. This way you could see quickly and without any tools how Google estimates your website. Even if only whole numbers were displayed in the Google Toolbar PageRank, it was a benchmark for many webmasters to measure themselves against the competition. However, Google removed this feature in 2016, the reason being that Google decided to use PageRank for internal purposes only.
An easy way to read out your own PageRank value is to use browser extensions. These can be downloaded differently depending on the browser. For example, when using the Google Chrome browser, the LRT Power*Trust is available as a free download. The tool providers themselves are responsible for the accuracy of the PageRank value of such tools.
More and more factors are included in the Google algorithm. Therefore, the relevance of the PageRank algorithm is decreasing more and more.
Website operators with financial means can buy backlinks or create several websites that link to their own website. This makes it much more difficult for smaller competitors to keep up with such competitors. Therefore, the method of PageRank does not necessarily represent the real quality of a website.
PageRank is vulnerable to link spamming from websites with a lower PageRank value. With a so-called nofollow attribute you can tell the crawler that it should not include the link to a website. This way you can control your PageRank yourself, even if only conditionally.
TrustRank, which was patented by Yahoo, is an alternative to Google’s PageRank. TrustRank is also based on inheritance, like PageRank. In contrast to Google PageRank, the TrustRank algorithm assumes that trustworthy websites only link to other trustworthy websites, and spam websites in turn only link to other spam websites. In this procedure, some trusted websites are selected manually. The further a link subsequently moves away from the selected trusted website, the more the website loses trust.
Another alternative to Google PageRank is the Hummingbird algorithm, which has been used by Google since 2013. According to Google, the new algorithm should include the old PageRank value.
You want to learn more about exciting topics?
