
SEO, Search Engine Optimization or Search Engine Optimization - you've probably heard these buzzwords from time to time. But what is behind it? What is SEO and why do you need it? You can read that and much more here. ... Continue reading
| 13 min |


| 15 min |
Google Analytics – What is it?
The web analytics in general
What insights do you get thanks to Google Analytics?
How does Google Analytics work?
How do you create a Google Analytics account?
How do you manage your Google Analytics account?
What is the goal of Google Analytics?
Advantages and disadvantages of Google Analytics
Why Google Analytics 4 (GA4)?
Roughly speaking, Google Analytics is a free tool from the Google Marketing Platform, which hosts several tools since the rebranding of Google Ads. It helps you to perform web analytics. In detail, this means that it allows you to analyze your online and marketing activities in-depth. Analytics is free in the basic version, but if you want to upgrade the tool to Analytics 360, it costs, like all 360 products of the Marketing Platform.
However, you can also use the tool very well for analyzes in the free version. Here it helps you especially to examine and track campaign successes and user behavior on your site. This makes it easier for you to find out where the strengths and weaknesses of your website lie. However, the continuous analysis can only be done by integrating the tracking code into the source code of your site. How exactly you have to proceed, you will learn in the First Steps guide from Google.
The days when a website was just a signboard are long gone. The fact is: your website is a real online marketing multi-talent. That’s why you should urgently exploit its full potential.
Best of all, you can target your content to a very specific audience – your target group. This is exactly where web analytics, also known as traffic analysis, comes in. This is preceded by so-called web tracking, i.e. the collection and recording of data on the web, which serves as the basis for subsequent analysis and evaluation. Web analytics should help you to control the success of your website in the long term and thus improve its efficiency.
Many online measures struggle with high wastage. These bring very little effort and ensure that you waste your resources unnecessarily. Thanks to current technologies, such as Google Analytics, you can take a closer look at these losses. This in turn helps you to plan and design all actions more precisely. By collecting data on the behavior of your website visitors, you can make an accurate analysis that will help you predict future behavior better. This in turn can clearly influence your decision-making process and help you monitor the success and optimization of your website.
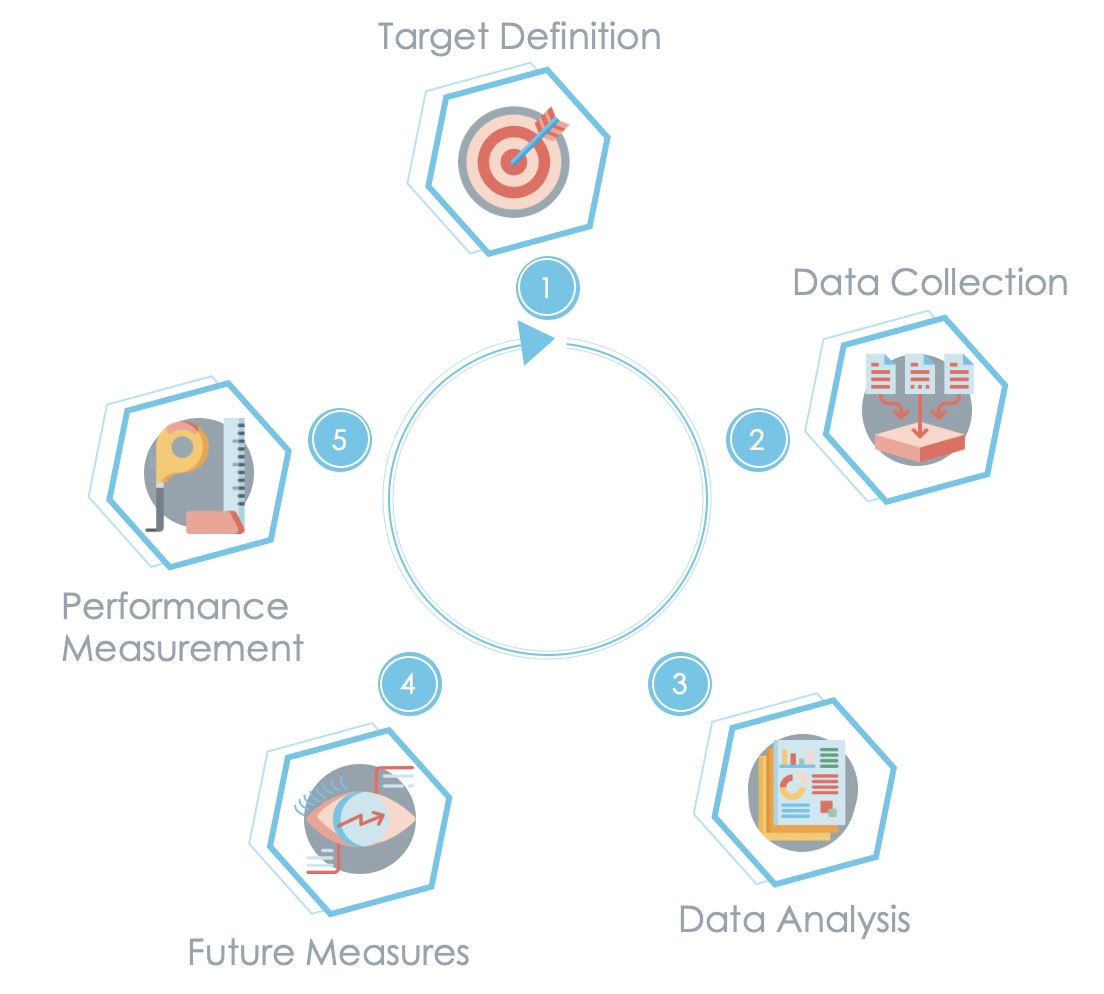
In summary, we can say that a certain cycle is created in web analysis. The definition of the goal is the starting point, whereupon data collection begins, which is subsequently interpreted. In the fourth step, measures are derived that determine future actions and procedures. This is followed by the measurement of success. After that, the process starts all over again in order to constantly improve and exploit all potentials.
Google Analytics gives you various insights. For example the following:
As a further function, you can define individual goals and measure your conversion rate, i.e. the ratio of visits or clicks to conversions. How exactly these goals look, however, is up to you. It can be newsletter signups, but also measuring the success of your marketing measures. In addition, you can now even link your social media channels with Google Analytics. This gives you a better overall picture of your performance.
Google is continuously improving its Analytics tool, which is why new features are added all the time. It is therefore important that you always stay up to date so that you don’t miss anything. You can find information about this on Google’s Analytics blog, for example.
Google Analytics does not collect personal data – many people often get this wrong. On the contrary, it is explicitly stated in the terms & conditions that these may not be linked to Google Analytics. In times of General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) this is in fact important to emphasize: Google Analytics never analyzes a single user but instead aggregated groups, values and trends. In addition, tracking is often blocked by different software programs, which is why the analyses give clear directions, but do not have to be 100% accurate.
The tool uses cookies for data collection, which are activated by the Google Analytics tracking code embedded on your website. First-party cookies are then stored with your visitors and regularly send information that is exclusively transmitted to Google Analytics. Since this is first of all raw data that does not really help you, it is processed in the second step. How this is done depends on your configurations. In the “Administration” section, you can therefore make various settings in three different levels within your account:
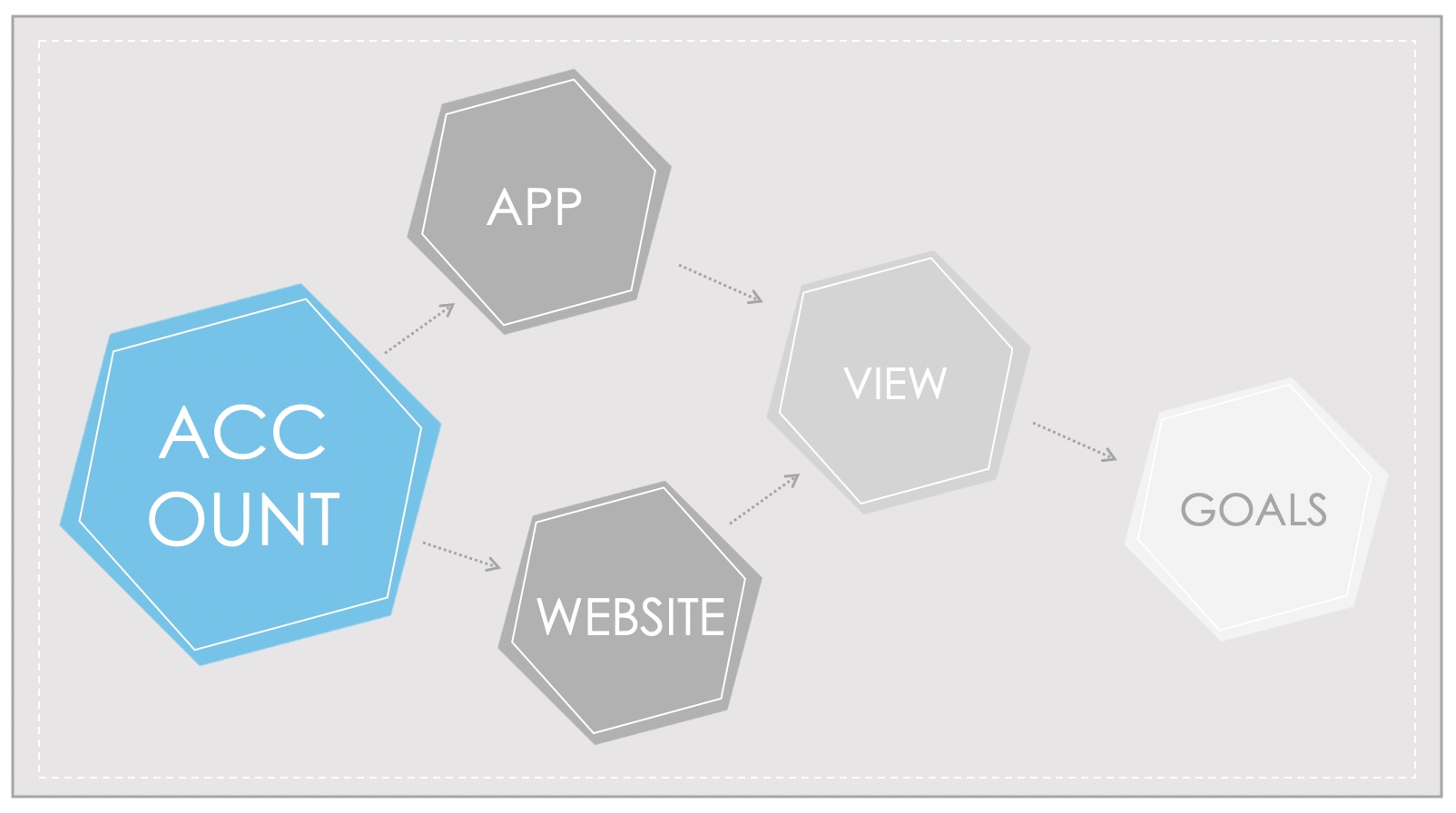
Each account can contain up to 100 Analytics accounts, 50 properties, 25 data views and 20 targets. You can define targets yourself under Data View.
As with Google Ads or similar Google tools, creating an account with Google Analytics is made really easy. If you already have a Gmail account or use another Google product with a different email address, you can log in with that. The login data you use here is valid for all Google products.
If you don’t have an account yet, you need to create one with a valid email address. You can do that easily here.
Once you have created the account and are logged in, you can log in via the Google Analytics website.
Now it’s time to set up the account. The following levels of organization are basic:
You will also be asked for different data shares in this step. It is advisable (and also recommended by Google) to check all of them. The reason for this is that you can later link other tools such as Google Ads, AdSense, etc. with your Analytics account. If you have problems with the tool, the technical support will help you. If you don’t want to check the box for any reason, that’s no issue either. If you need assistance from support, you can also release your account to them at the appropriate time.
Once you have set everything up, you can retrieve the tracking ID – by the way, this is also the name of the tab you have to click for this. After you have confirmed the terms of use, you will receive your individual UA number and a Google Analytics tracking code. You insert this in the source code of all pages of your website that you want to analyze. Copy the code and paste it immediately after the tag. In order to collect all information in a privacy compliant way, you have to add the code extension “anonymizeIP” and set it to “True”. Alternatively, you can insert the UA number using the previously installed Google Tag Manager.
For data protection, it is also important that you conclude an Analytics contract with Google and place the adapted privacy policy on your website in an easily accessible manner. You can easily conclude the contract online. These are the steps you need to take:
Via the user settings, which you can recognize by the cogwheel symbol, you can make changes to your data even after creating the account.
Your account is divided into three main sections:
On the home page, you can see your Analytics accounts with their properties, apps, and data views. You get a complete overview of all analytics here.
In the Customizations tab, as the name suggests, you can make custom configurations and set up different dashboards.
Under Reports you can call up various evaluations in report form. Here you not only get an insight into the classic standard reports, but you can also make individual and personalized configurations.
The main goal of using Google Analytics is to collect solid data that you can then use as a basis for future actions. With these insights, you can plan, gain a deeper understanding and constantly optimize your website.
The target project was developed specifically for this purpose. The whole thing works as follows: You define your personal goals, then you can use Google Analytics to determine how well they are being achieved. This is important because you cannot measure success without specified goals. It therefore makes sense that you think clearly about the topic of company goals and define them unambiguously. The company goals are the basis for defining the website goals. These can then be subdivided into micro and macro goals. By evaluating your goals, you can then develop key figures that make it easier for you to recognize successes and compare them in the future.
Keep in mind: Google Analytics goals do not always have to be identical to website goals, as the focus here is on purely technical aspects.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
Option to export all analyses | Data must be exported for secure, permanent storage |
Link with Google Ads for better analysis of paid advertising | Uses of the collected data unknown |
AdSense integration | Storage of data on US servers |
Social media integration | Complex handling of the tool for laymen |
Measurement of loading times | Complex configuration for laymen |
E-Commerce-Tracking | Google as a data leech |
Definition of individual goals | Paid variant could be expensive for smaller companies |
Measurement of individual goals | |
InPage analyses | |
Better understanding of the overall user picture | |
Simplified analysis of special events | |
Working in a team possible | |
Free of charge in the basic version | |
Custom reports can be created |
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the latest version of Google’s analytics tool. Unlike the previous version, Universal Analytics, GA4 is based on a completely new technology and offers advanced features for analyzing data.
At the heart of GA4 is the event-based model. Instead of focusing solely on page views, GA4 captures various events that occur on a website or in an app. For example, these events can be page views, clicks, interactions, conversion events, or custom actions. This allows more detailed information about user behavior and interactions to be captured.
GA4 also uses a more flexible data model. It allows data to be collected and analyzed across multiple platforms, including websites, mobile apps, and even offline sources. This allows companies to get a more comprehensive picture of the customer journey and track user behavior across different channels.
Another important feature of GA4 is the integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence. The tool provides automated insights and predictive models to identify patterns and trends in the data. This makes it easier to identify target audiences, optimize marketing campaigns and improve user experience.
In addition, GA4 offers enhanced privacy and data retention capabilities. It is better designed to comply with data protection regulations such as the GDPR and offers more control over data processing and retention.
Overall, Google Analytics 4 provides powerful data analysis tools and features to help businesses gain insights into user behavior, optimize marketing strategies, and improve the customer experience.
ATTENTION: Change from Universal Analytics to GA4 🚩
As of 01.07.2023, data will no longer be collected for Properties in Universal Analytics. It is therefore mandatory to switch to GA4 if Google is to continue to be used as an analytics tool. As of 07/01/2023, users will only have access to the previously collected data for 6 months. To avoid data loss, we recommend exporting all previously collected data by then. For users using Universal Analytics 360, the processing period will end exactly one year later, on 01.07.2024. We recommend everyone to switch over as early as possible to avoid data loss.
If you have any questions, we will be happy to help you and find an individual solution for your company. ⏳🚀
You want to learn how to use date to optimize your website for search engines?

