
Get tips and tricks to get the most out of your Google reviews. Learn why they are so important, how to deal with negative reviews and how to get more reviews! ... Continue reading
| 18 min |


| 25 min |
What influences creativity?
Game rules of ideation – Here’s what you need to keep in mind
Idea killers, that limit you in your creativity
Types of creativity techniques
Creativity for individuals
Creativity techniques for teams
Creativity techniques for large groups
It’s the foundation of a successful content marketing strategy: A good idea. Creativity is a fundamental component of good, user-focused content. Everyone can be creative in their own unique way, even if it doesn’t feel that way to everyone. Sure, it’s not always easy. Especially when developing completely new content strategies, it’s often hard to shed the typical tunnel vision, think outside the box, and come up with something truly new. Even the most imaginative minds sometimes reach their limits. But don’t worry! That’s why there are several creativity techniques to help you find new input and come up with innovative concepts.
Using the 4P model, we can see that there are several factors that influence creativity.
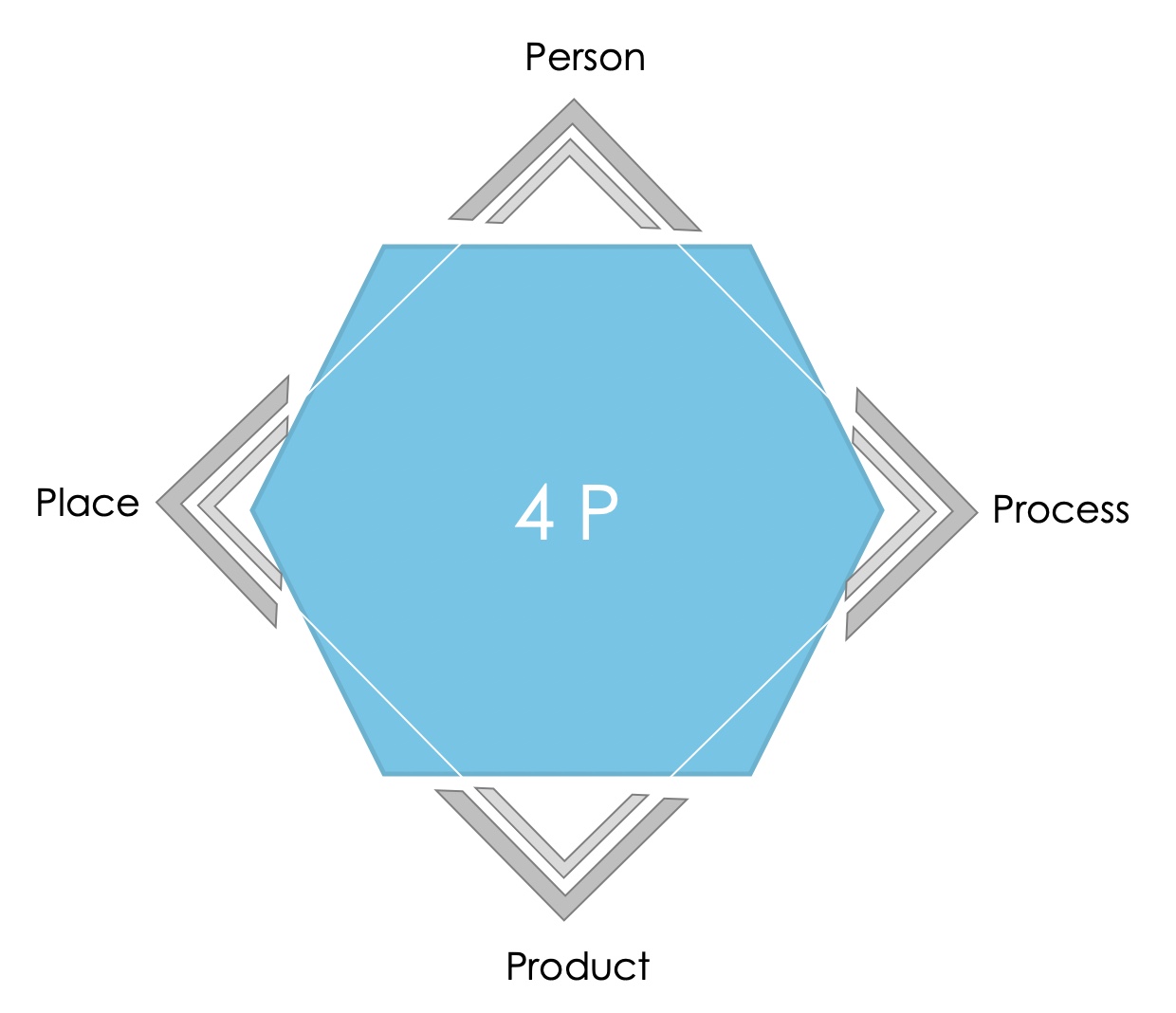
So there are different frameworks. For better development, you should definitely make sure that you work in a quiet and undisturbed atmosphere. Cell phones, telephones or anything else that interrupts the thought process and distracts you unnecessarily are therefore taboo. In addition, you should make sure that the group size is appropriate. Depending on the technology, the optimal number of participants varies. You also need to set a time frame for the creative session. If in doubt, this is not enough, you can always set an additional date.
The number one rule of ideation is “Every thought counts. There are no evaluations.” Principle is only evaluated in the aftermath, which is really useful and useful. This is the only way to collect as many ideas as possible in the first step. There must be no criticism, otherwise participants are afraid to freely express what they think. Also, there are no taboos or prohibitions. There is nothing that is too outlandish or too abstract. Every idea is important and valuable.
In order to engage optimally in the creative process, various idea killers must be eliminated. Most often, these are barriers in the mind and entrenched rails that are difficult to discard. You should therefore try to avoid the following:
Creativity techniques serve primarily as a supportive tool in the process of idea generation or collection. They are used as a thinking aid, but do not promote the quality of the generated ideas, but only the quantity, with which subsequently increase the chance of good innovations. They can be carried out, both, alone and in teams. Creativity techniques are distinguished into:
Intuitive methods generate many ideas in a short time through thought associations, as they activate the subconscious. Thereby, the possibility exists over the thinking outside the box and eliminate an entrenched way of thinking.
On the other hand is the discursive method. Creativity techniques that are classified here are systematically carried out. For this reason, they provide less output in the same amount of time. However, these are all-encompassing and illuminate problems from all sides.
The combination methods combine intuitive and discursive elements.

Clustering indirectly belongs to brainstorming and is sometimes combined with mind mapping. Therefore, it is also similar to these methods in terms of the process. As with a mind map, it is mainly about visualization. Therefore, write the central word in the middle of a sheet. On the outside you keep all keywords in association chains, in order to represent the connections between the individual creative impulses ideally. These chains provide a link between conceptual and pictorial thinking, i.e. between the left and right hemispheres of the brain, and thus create an even broader creative process.

It’s as simple, as it sounds: a diary for ideas. To do this, use a notebook or notepad and record every thought that comes to mind about a particular problem. In this way you avoid in a very simple way that it slips away from you again. It also gives you the possibility to recall ideas at any time, to check them, to organize them, and to systematically pick up again and implement.
Of course, instead of a book, you can choose a tech alternative. Apps like Evernote, OneNote, SimpleNote or Workflowy can be used just as well and sometimes even make you more flexible than a book. What you can work better with, of course, depends on you alone. Just try it out for yourself.

Mind maps are among the best-known creativity techniques. They are a kind of memory or idea map and help to open up and visually represent a certain subject area. The “problem” or the keyword for which the ideas are to be generated is found in the center. With the help of links, the connections to other terms around the main word are shown. Often, this connection from the center leads to superordinate categories, which are then in turn broken down into further annotations, similar to a tree diagram, that serve as explanations or supplements.

Synectics, or merging, is a relatively unknown creativity technique. Nevertheless, you should not underestimate it. This method promotes unconsciously running processes, by alienating the familiar through analogies step by step. So the unfamiliar is made familiar. This is at the same time the basic principle of this technique. Through this modification, a factual distance to the problem and existing solutions are created, in order to generate free space for the creation of something new.
You can also use synectics as a complement to Mind Map. In this case, words are written in the corners of the mind map sheet. From the main word in the center, you have to create connections to these abstract terms must be created. So you can easily expand your horizons.
A synectic collection of materials can additionally help. This consists of visualizations, sounds, noises, videos, objects, words, etc. It is completely free in terms of content and should serve as food for thought. You can form associations about objects in this collection and thus generate new ideas.

This creativity technique builds on an already existing product, which is modified systematically and playfully-experimentally. This way, you can work your way along the checklist and thus have a good guideline that promotes your creativity. A typical version of the Osborn checklist is the following:
APPROACH | QUESTION |
|---|---|
Other Use | What are the alternative uses of the product when it remains as it is or is adapted? |
Customize | Are there parallels in the past that can revive something that can be copied, imitated or replicated? |
Modify | Are there new turns, directions that can be taken with the product or new shapes, colors, movements, etc.? |
Enlarge | Can something be added or the time period, cycle, frame be changed or something be made more stable, firmer, stronger or something be increased, lengthened, thickened, etc. or value added to the product or something be duplicated or multiplied? |
Reduce | Can something be condensed, flattened, shortened, slimmed down, etc. or be rationalized or comitted? |
Replace | By whom or what can something be replaced? Are there other materials, ingredients, contents or places or approaches or driving sources or sounds, tones, etc. or manufacturing methods, processes? |
Rearrange | Can components be exchanged or a new scheme, model, layout, etc. be developed or cause and effect be swapped or the sequence/ranking be changed? |
Invert | Can you swap positive and negative or reverse something to the opposite or turn something upside down or reverse roles and tasks? |
Combine | Can units be combined or intentions and areas of application be combined or ideas, approaches, partial solutions be combined? |

In this technique, you use your imagination to picture the idea or end result/product in as much detail as possible. Letting your imagination run free is not easy for everyone. But you can train it! Try to look closely at your surroundings and, for example, interpret something in the shapes of clouds, trees or landscapes. Notice things consciously and sharpen your sense of sight. Daydreaming is also allowed and a good way to improve your imagination.

Sometimes all it takes is a little exercise and fresh air to come up with good and new ideas. Studies show that physical activity has a positive influence on the mental state and creativity.

The main goal of the ALPEN method is improved daily time management. This is especially important for one reason: Only if you are not under time pressure, you can be creative.
ALPEN is thereby an acronym and stands for the following:
A – Write down activities and tasks, create to-do list
L – Estimate length (time required)
P – Keep buffer time free (best about 40% of total work time)
E – Make decisions and set priorities
N – Schedule follow-up checks and unfinished items for the following day

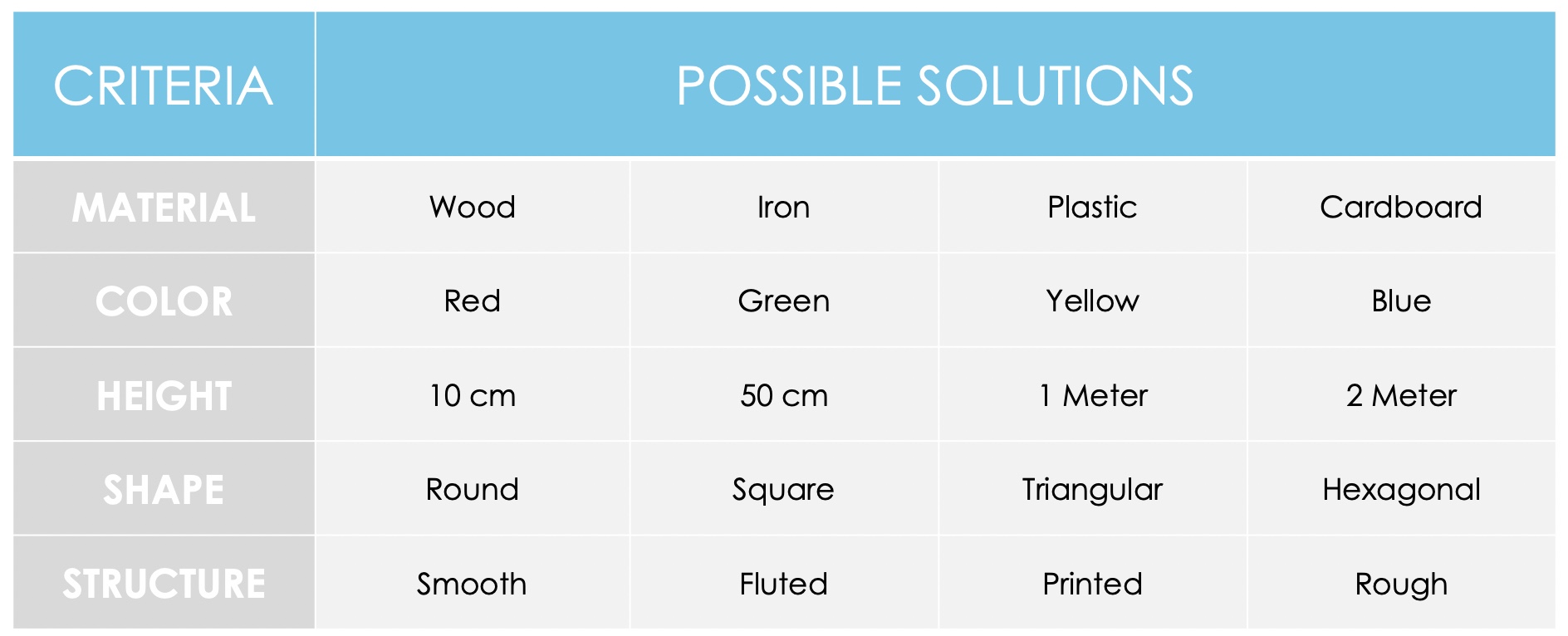
This technique is a multidimensional matrix, which illuminates different aspects and thus should show new combination possibilities. This is especially helpful with already existing products, since you get a new perspective. But this method is also suitable for generating ideas.
The matrix of a product might therefore look like this:
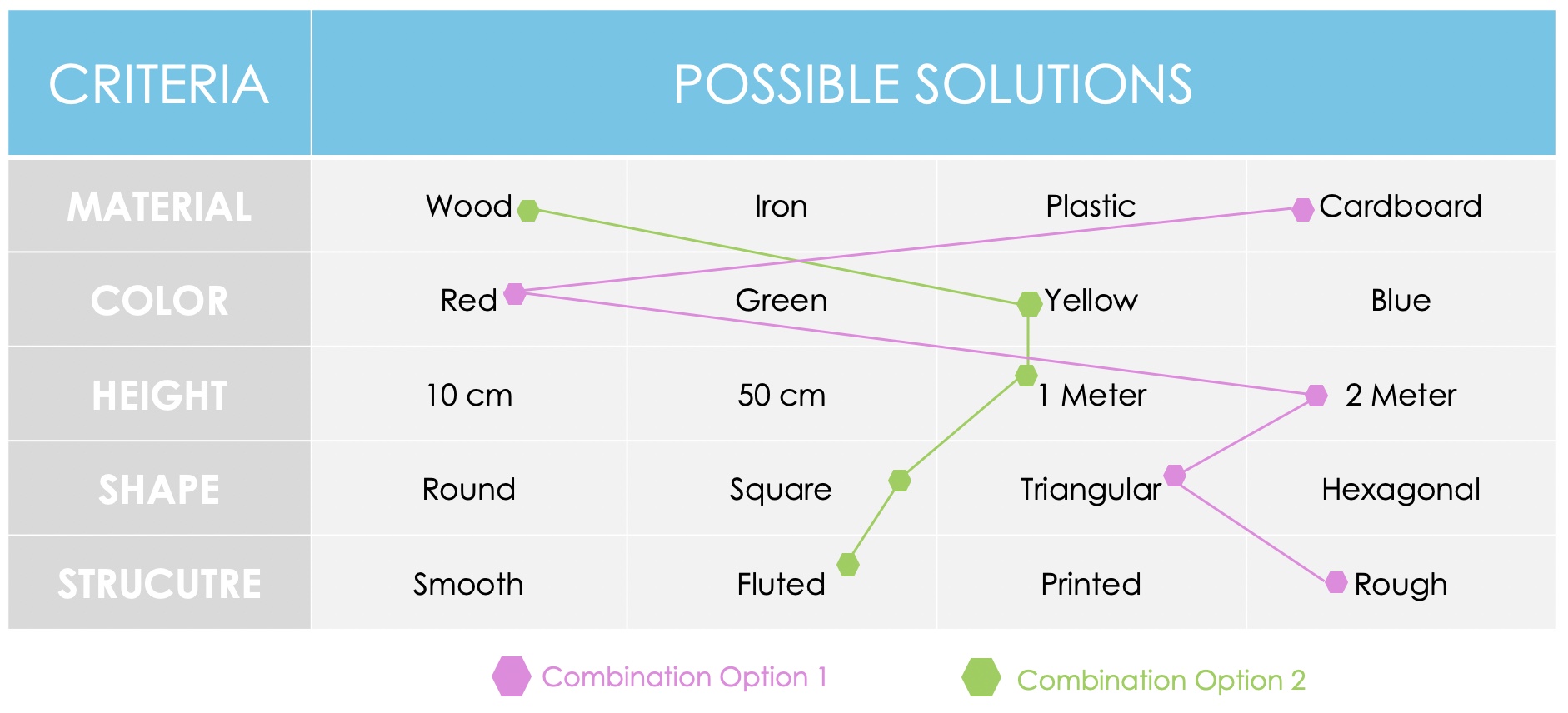
Once you have worked out all the criteria and possible solutions, you can go on to the possible combinations that the product can take on.

If you have the feeling that you cannot develop creatively, this is possibly due to blockages, which limit you. With the problem solving tree you can therefore solve these problems. This way you create a structure helps you find out what the issue is. Through the detailed view and different stations of the tree individually and weight them. The problem-solving tree is created in three phases:

1. The Root: Here is the problem or task definition written down.
2. The Branches: Extend the tree to include technical and structural parts that are part of the problem
(can be created through brainstorming).
3. The Gaps: Gaps between the branches and the tree should now be eliminated by creating connections of the individual parts. This will give you new ideas, and you can find new ideas.

The idea is simple: six participants each receive a sheet on which three ideas must be written down. These sheets then rotate a total of five times within the team. In round one, everyone thus develops their own ideas. In the following five rounds, however, the ideas of the predecessors are then taken up again, expanded and further developed.
Once each participant has had each sheet, the discussion phase begins, in which all ideas are analyzed and evaluated.

The ABC method is not only used to find ideas, but also helps to evaluate ideas and to give feedback. It works quite simply: You write all letters of the alphabet vertically under each other on a piece of paper, then you write down impulsively everything that you associate with the respective letter and the task. The association must always start with the letter you are at. Afterwards, each participant explains briefly and concisely what the intention of his idea was. Finally, a discussion round is introduced in which all ideas are discussed and evaluated.

Brainstorming is the most widely used and well-known creativity technique. It is the absolute classic for several reasons:
It works as follows: Each participant gradually, over a period of time, gives spontaneously all ideas for the solution of a concrete problem or to a
predefined task. This often results in combinations of ideas from the suggestions of several members, and the results become more and more detailed and appropriate.
The process consists of two steps:

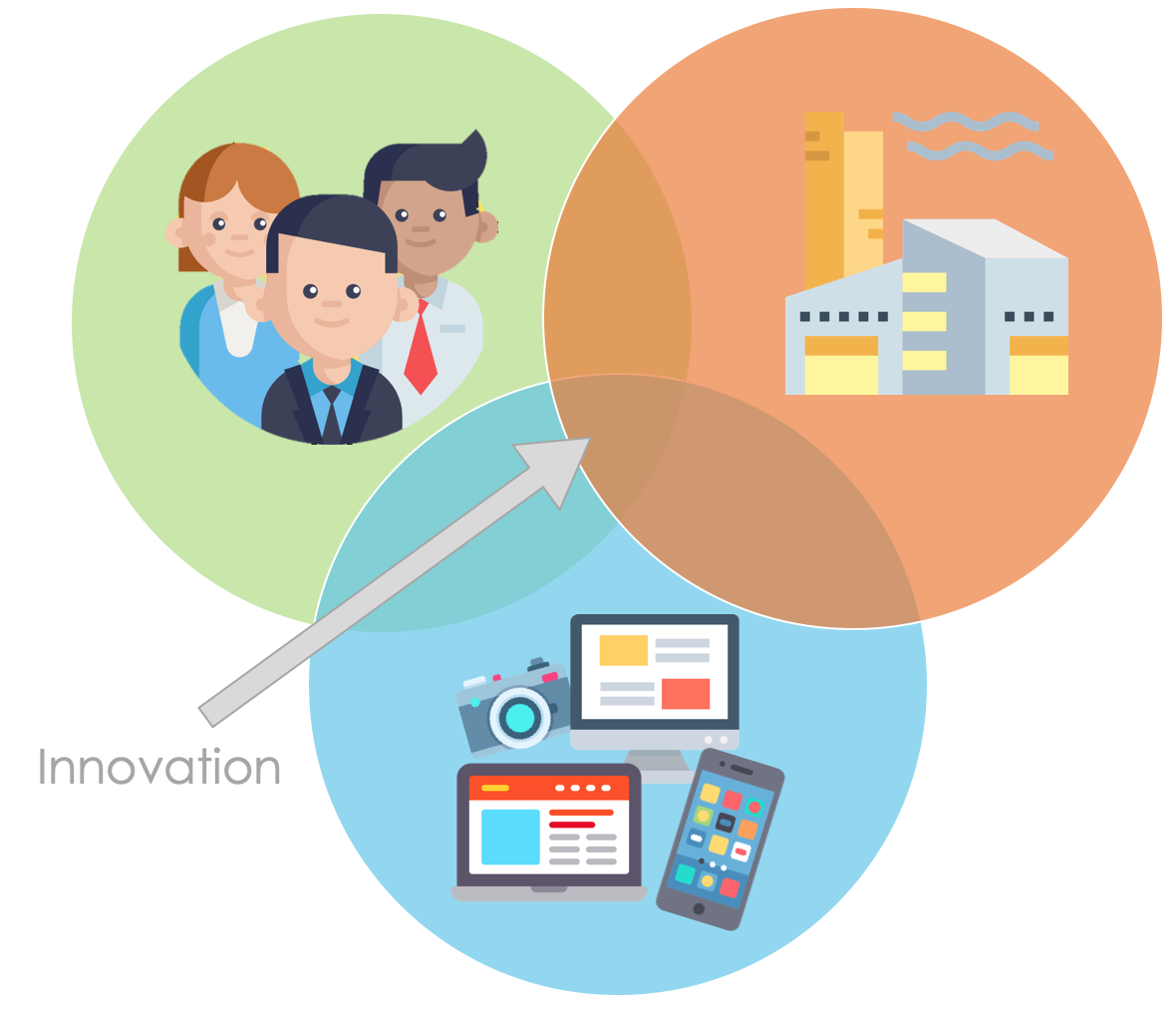
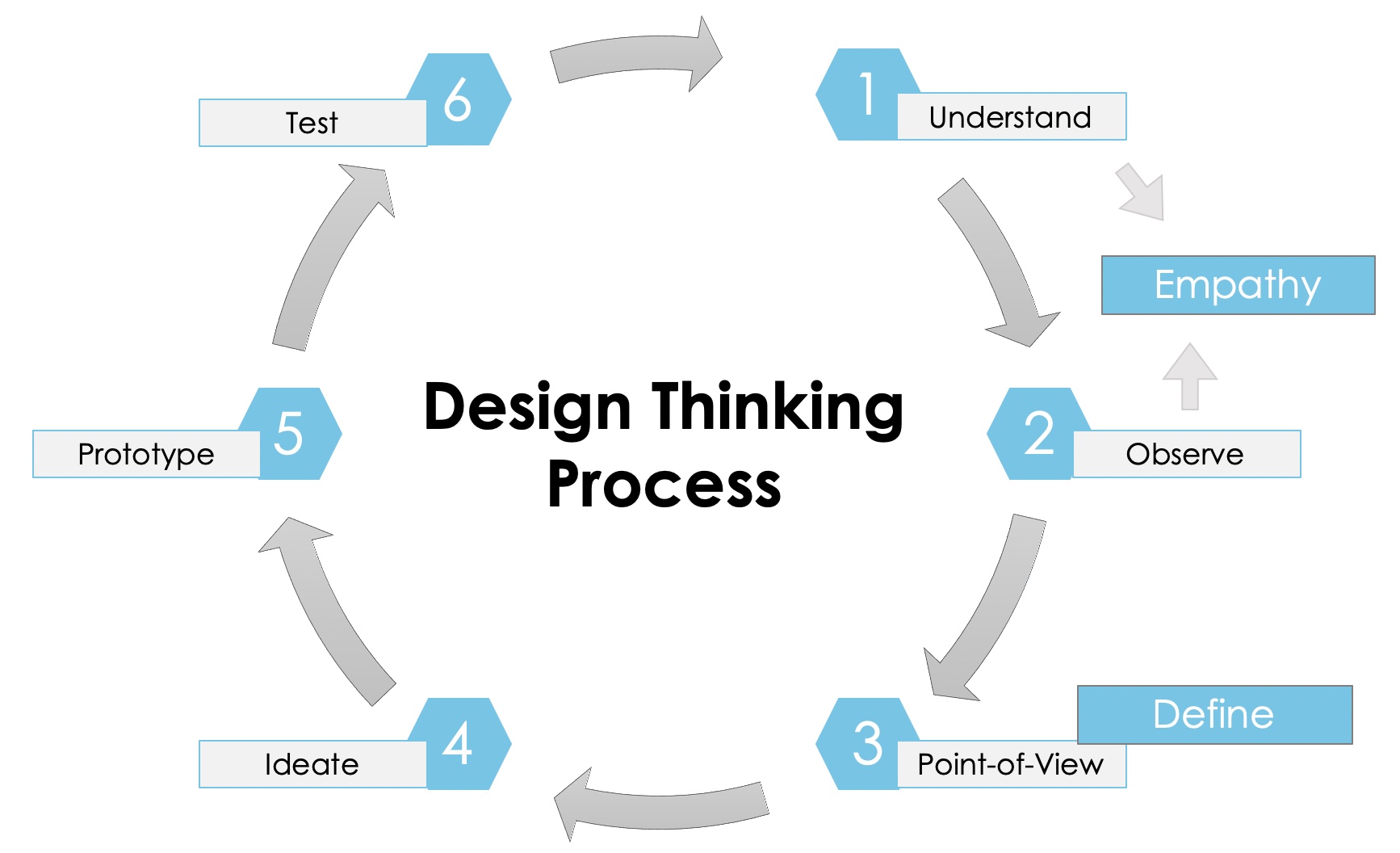
Design Thinking deals with the three factors “people”, “technology” and “business”. Thus, as many viewpoints and perspectives as possible should be incorporated into the problem-solving process. In this method, the innovation and idea arise from the intersection of these three elements. As a result, it combines attractiveness, feasibility, and cost-effectiveness, while still remaining people-oriented.
There are several steps that need to be gone through for the design thinking process to work optimally. These do not necessarily have to be followed in the given order, but can be worked through in a jumbled fashion. Furthermore, jumping back and forth between phases is allowed. There are two different models that represent these phases. One consists of five steps, the other of six steps.
1. Understand
2. Observe (“Understand” and “Observe” are combined into “Empathy” in the 5-phase model).
3. Point-of-View (also called “Define” in the 5-step model)
4. Ideate
5. Prototype
6. Test

From the structure, brainwriting is very much like the brainstorming technique. Unlike brainstorming, however, each participant has quiet time to collect and write down his or her ideas. There are three phases in the process of brainwriting:

Sketchnotes means something like sketch notes. The name says it all. As you can see in the following example, this creativity technique is mainly about visualizing your thoughts.
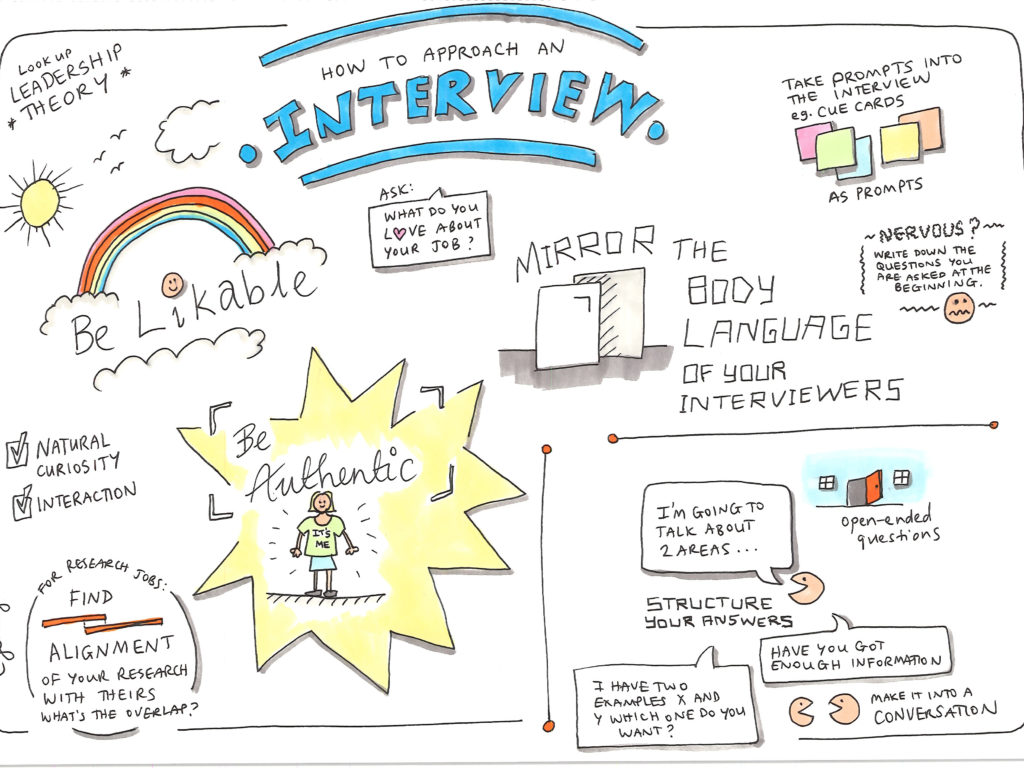
The visualization of ideas primarily helps you to remember them better. It also makes connections more understandable and makes it easier for you to keep track of your notes.

This method is intended to stimulate a group discussion. A kind of role play is created, in which each person of the team represents a different opinion. For this purpose, the hats, which represent different opinions, distributed and afterwards in different rounds always passed on to the next person.
The following “hats” exist in this process:
| HAT | CHARACTERISTICS | MEANING |
|---|---|---|
| White | •Analytical thinking Concentration on facts Objective attitude | Gathers information without judging it Data and facts |
| Red | Emotional thinking and receiving Concentration on feelings Subjective attitude | Both positive and negative feelings Gut feeling counts |
| Green | Creative, associative thinking New ideas Constructive attitude | Crazy and unrealistic allowed → everything that brings new ideas |
| Blue | Orderly, moderating thinking Overview of processes Big picture attitude | Is on the meta-level to monitor, analyze and evaluate |
| Yellow | Optimistic thinking Best case scenarios Speculative attitude | Objective consideration of the positive aspects |
| Black | Critical thinking Describing risks, problems, skepticism, criticism and fears Objective attitude | Objectively examines all negative aspects Avoid personal feelings |
As you can see, there are three 3 complementary ways of thinking:

Walt Disney is not only the creator of the most famous children’s movies, he also developed a creativity technique that is supposed to help loosen stuck thought structures and look at things from a new perspective.
For this, the participants take on different roles:
ROLE | MEANING |
|---|---|
Dreamer | EVERYTHING IS POSSIBLE! Sees neither problems nor risks and imagination has no limits |
Realist | LET’S GO! At the same time a doer and practical & neutral point of view |
Critic | WAIT A MINUTE… Look for stumbling blocks and contradictions and looks where problems lurk |
When practicing this technique alone, all roles must be taken once. In teams, too, everyone must take on each perspective once. A neutral observer should also be present in the team to record all thoughts and moderate the process.

The Flip-Flop method is also called the inversion method or headstand technique. It serves not only to find ideas, but also to solve problems. Here
the original question turns into the exact opposite. This comes from the fact that human beings, due to a naturally innate pessimistic attitude,
discover problems, errors and resistances of a project much easier. Opportunities, solutions or possible development steps, on the other hand, are not so easily uncovered.
The Flip-Flop method consists of four phases:

The stimulus word technique belongs to the association techniques and offers the possibility to be creative in a relatively simple way. This is how you proceed:

A collective notebook is, as the name suggests, for the public. It’s in a freely accessible place or passed around so that everyone can write their ideas in there or expand on other team members’ suggestions.

The point of a Brainstation is about all members of a group having to go through different stations one after the other. At each of these places, a
different problem, or the same problem, just looked at from different angles, is viewed at. Depending on where you started, you build up completely new ideas or supplements those of previous participants.
There are also two variations of the brainstation technique:

In this technique, participants jointly and piece by piece develop a kind of graphic that is intended to visualize the problem more precisely. This is created primarily by “pinning down” the core issue and illuminating it from two sides. The visualization therefore has a clear structure:
To get to the solutions, there are several fixation options that indicate the way in which the problem should be illuminated:
Which of these creativity techniques is best suited for you and/or your team is up to you. It’s best to try out different methods to find out for the future which ones suit you best and with which ones you get the best output. If you feel stuck again, you can change your tactics and switch to another technique.
Use these creativity techniques to create fantastic content!
