A relaunch offers you the opportunity to optimize products, logos, websites and brands. Learn more about it here! ... Continue reading


IP stands for Internet Protocol and is an individual address that uniquely identifies a device on the Internet. Thus, the Internet protocol forms the basis for devices to be able to communicate with each other globally.
What does this mean in concrete terms?
Imagine a large room with many people. Each person represents a computer and has a name tag with his or her first and last name, which uniquely identifies the person. If I now want to send another person information in the form of a data packet, I can identify them uniquely by their name – i.e., their IP address. This guarantees that no other person in the room will receive the information. Thus, the Internet Protocol provides the basis for a targeted exchange of information among all users.
The MAC address is the physical address of a device within a network. With the help of this address, incoming data packets within a network can be assigned to the correct device.
What does this mean in concrete terms?
In a family household, several devices, such as laptops, are on the same network. While the father works on the laptop via home office, the son inquires on different domains about leisure activities in his area. In order to provide both of them with a good user experience (UX), it is important that the two laptops only receive the exact data packets that they have requested. The father only wants to see information about his work on his browser screen, while the boy only wants to read information about sports clubs. In order for the incoming data packets from the Internet to be assigned to the correct device, physical addresses of the devices are required within a network – these are precisely the MAC addresses.
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol. This is a network protocol that refers to layer 2 of the OSI model. This protocol is required to send data packets between individual hosts within a local area network (LAN). The IPv4 protocol lacks the ability to store the device address due to its limited length. Therefore the ARP and its cache mechanism is used for this purpose.
What does this mean in concrete terms?
The ARP protocol enables the exchange of data between individual laptops in a network, for example within an office or household.
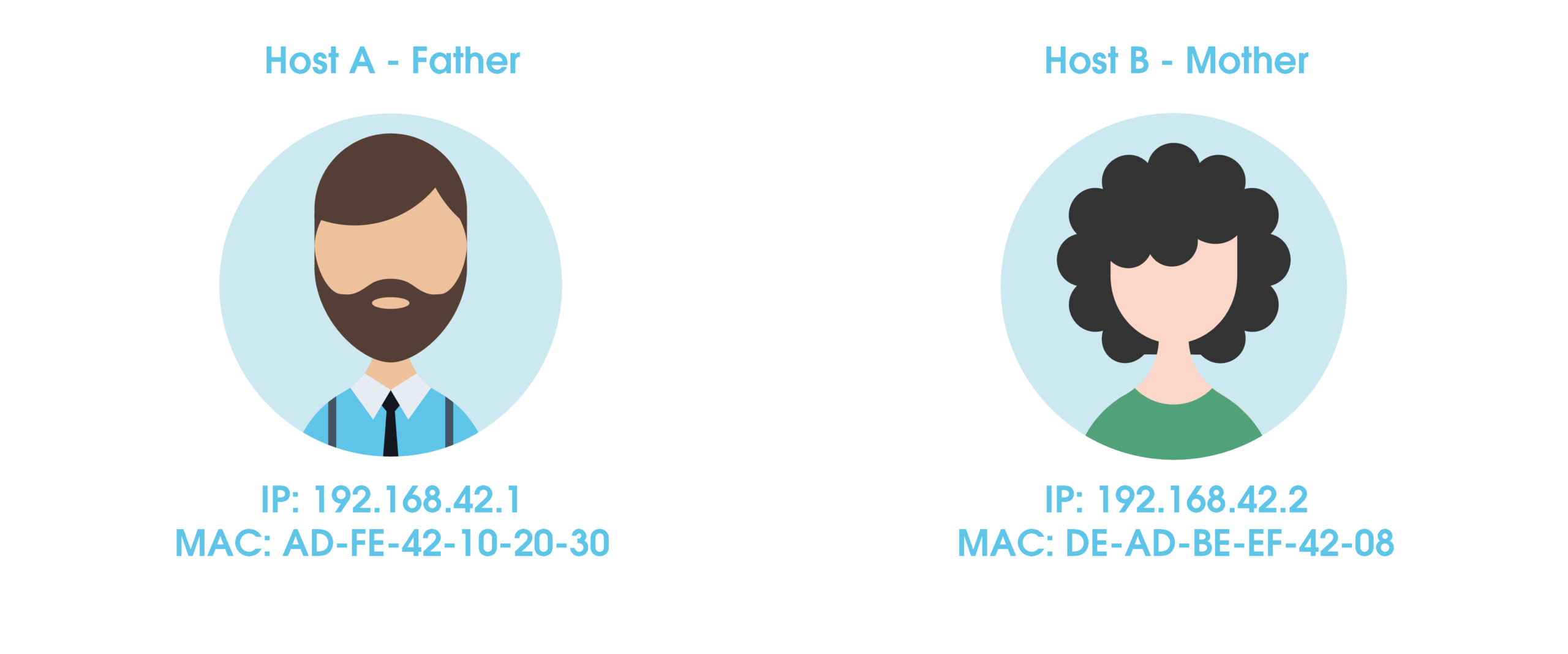
An example scenario: A network with two devices is considered. Both parents are at home with their laptops in the same network. The devices have the following attributes:
You want to learn more about exciting topics?